Advancing Anode Assembly Fabrication
A look at the science of conforming anode assembly for chrome plating.
Fabricating a conforming anode assembly is a necessary step when chrome plating injection and compression molds, but not all plating operations approach this step in the same way.
While a conforming anode is only one element in the electroplating process, the quality of the assembly strongly impacts certain critical parameters, such as plating film thickness, uniformity over geometrically complex molding surfaces and pitting control. Anode materials have evolved, but the current standard for functional plating of molding surfaces is still a system of individual, steel-wire anodes.
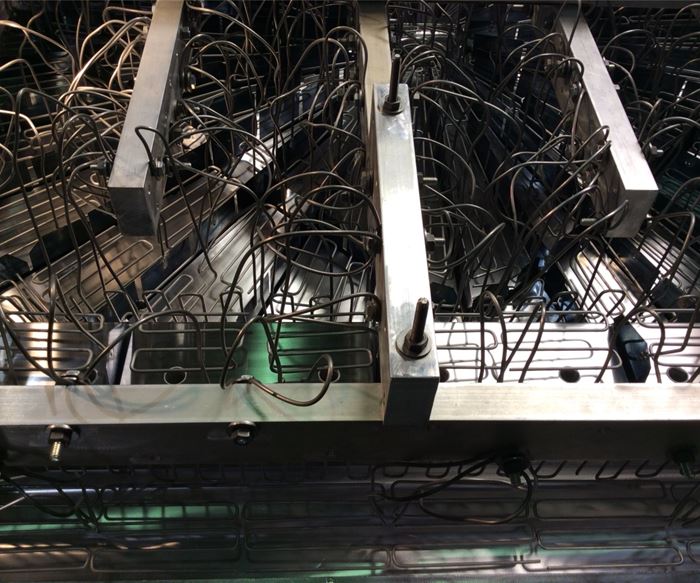
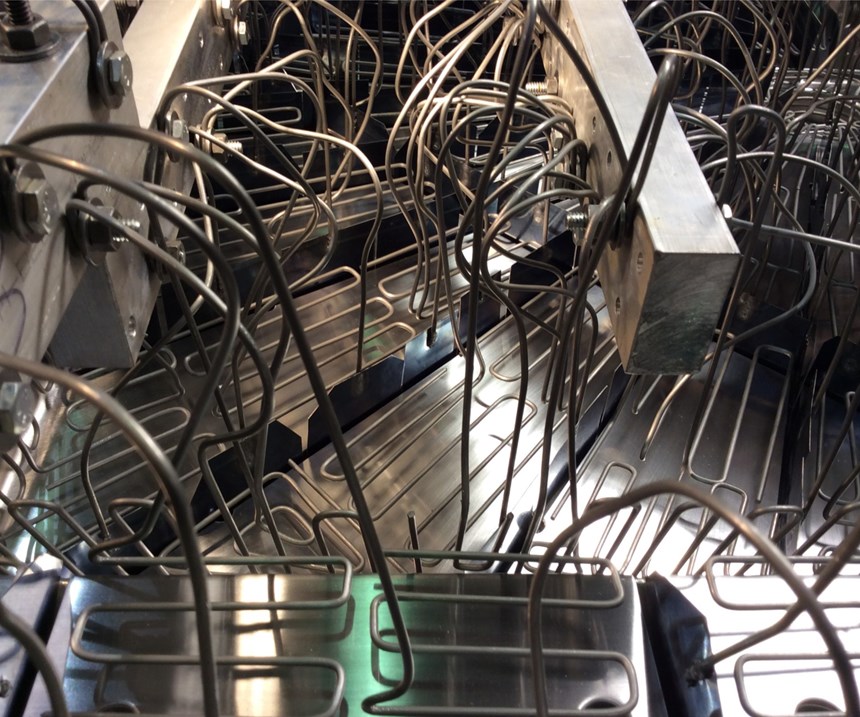
Platers used to fabricate anodes with malleable, perforated lead sheets. These sheets worked to a point, but some people believed they had a potentially unsafe impact on the working environment. An ISO14001-registered operation has incentives to seek alternative options, like custom-building the anode assemblies on a base frame of square, aluminum bars with mild, steel-bent wires that are individually attached to the frame and conformed to the tool’s specific geometry, for example.
Aluminum as a choice for the frame yields a more-even current distribution throughout the assembly, which has a significant impact on minimizing pitting in the plated surface. Minimal pitting is a primary performance requirement for many customers’ projects, especially for in-mold finishing tools.
Aluminum as a choice for the frame yields a more-even current distribution throughout the assembly, which has a significant impact on minimizing pitting in the plated surface.
The number of wires that are required depends on what it takes to conform to the geometry, which can be 300 or more for a large, complex tool, like a fiberglass bathtub or for an automotive body panel. This network of individual wires makes it possible for the overall assembly to become an inverse duplicate of the forms to be plated, which is critical for maintaining a consistent plating thickness within a narrow tolerance range over very geometric, complex surfaces.
As with every mature process, there is always room to evolve. The anode component of the plating process is no exception. For example, many chrome-plated tools, especially those for high-percentage, glass-filled parts, have grooves for stiffening ribs in the molded component. These grooves can experience release failure well before the rest of the mold. Reliably chrome plating the grooves to the same tolerances as the rest of mold will increase the lifecycle and maintenance intervals, and improved release and resin flow will decrease cycle time.
One solution for accomplishing these benefits is a system of individual blade anodes that rests within the grooves. This common method has been refined to enable the blades to remain centered within the grooves while submerged in the plating bath. This is a critical step for preventing the blades from contacting the mold and causing burning of the groove faces, which leads to unplated areas or inconsistent film thickness within the grooves. Another refinement addresses the current differential between the wire and blade anodes, ensuring uniform plating thickness with both anode types.
Molds with grooves for stiffening ribs that use these methods can yield groove-wear patterns consistent with the wear on the rest of the mold, which improves molding performance, tool life cycle and maintenance intervals.
About the Contributor
Luis Gonzalez is president of Surfacetec.
Related Content
What is Scientific Maintenance? Part 2
Part two of this three-part series explains specific data that toolrooms must collect, analyze and use to truly advance to a scientific maintenance culture where you can measure real data and drive decisions.
Read MoreLaser Welding Versus Micro Welding
The latest battle in finely detailed restoration/repair of mold materials.
Read MoreMachine Hammer Peening Automates Mold Polishing
A polishing automation solution eliminates hand work, accelerates milling operations and controls surface geometries.
Read MoreThink Safety: Eliminate Hazards Throughout the Shop
The tooling community is taking advantage of new products for safer mold shops and molding facilities.
Read MoreRead Next
How to Use Continuing Education to Remain Competitive in Moldmaking
Continued training helps moldmakers make tooling decisions and properly use the latest cutting tool to efficiently machine high-quality molds.
Read MoreHow to Use Strategic Planning Tools, Data to Manage the Human Side of Business
Q&A with Marion Wells, MMT EAB member and founder of Human Asset Management.
Read MoreAre You a Moldmaker Considering 3D Printing? Consider the 3D Printing Workshop at NPE2024
Presentations will cover 3D printing for mold tooling, material innovation, product development, bridge production and full-scale, high-volume additive manufacturing.
Read More