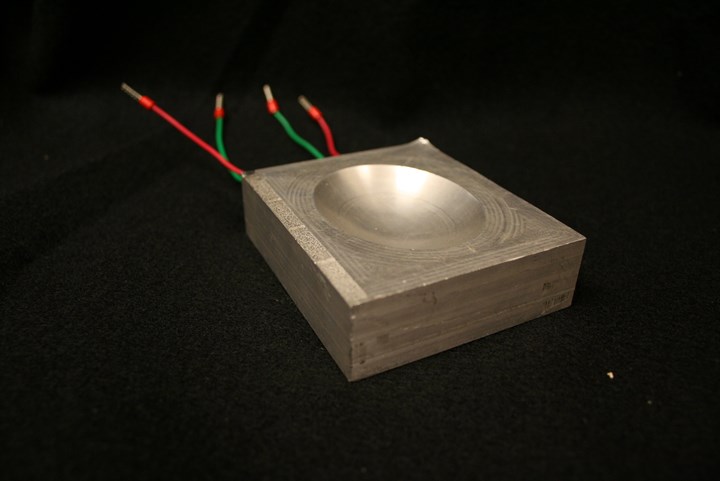
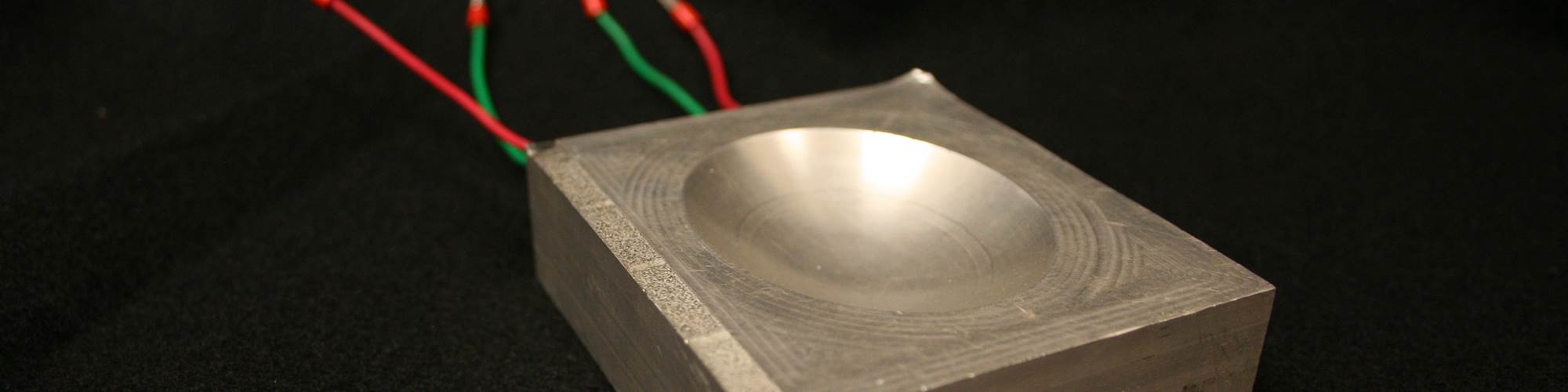
Half of an injection mold with embedded sensors. Photo Credit: Fabrisonic
Ultrasonic AM is a hybrid additive and subtractive system which adds a welding or printing head to its CNC milling platform. A unique process, the print head is able to print metal at room temperature. This process is also called solid-state welding because it happens in the solid form. No melting is occurring.
This true welding process is based on ultrasonic welding developed in the 1960s for electronic circuits. The wire-bonding process essentially uses ultrasound at room temperature to weld metal.
Printing at room temperature is essential because when you heat a metal, you change its properties. When you heat a metal to its melting point and then resolidify the metal, you really change its properties. Many printing processes that melt metal have metallurgical concerns because they are heating and cooling, making miles of weld. Ultrasonic AM does not melt, so the material coming in is the same as the material going out, albeit a different shape. This process does not heat up, so it is not changing any properties of the metal.
Ultrasonic AM does not melt, so the material coming in is the same as the material going out, albeit a different shape.
Not melting or performing this process at a low temperature offers the ability to embed components. With ultrasonic AM, you can lay down an electronic circuit, print metal directly over it and because the metal is not getting hot, it won't get damaged. This process is used to embed sensors and electronics, which translates into molds.
You can use ultrasonic AM to embed temperature sensors anywhere in a metal part that you are printing and receive continuous data from that sensor while it's in operation. Many shops conduct engineering studies using this technology to determine how a mold is performing.
For example, ultrasonic AM has been used for over a decade to embed sensors into parts that are on airplanes, satellites and nuclear reactors. It is the same concept as it would be with a mold: you want to get a sensor in a specific location and measure data during that product's life.
Another example is embedding temperature and pressure sensors in molds using a strain sensor or a strain gauge to back out pressures. However, once you embed the sensor, it is there for the tool's life, as it is embedded in solid metal.
Another application for ultrasonic AM is welding dissimilar metals, where one layer is aluminum, another is copper and still, another is stainless steel. Most welding processes cannot bond dissimilar metals. If using a fusion or arc-welding process to melt and solidify, those metals will mix and make something unusable.
If you don't have to print it, don't. Use the appropriate tools in your arsenal.
Ultrasonic AM can layer different metals together to improve mold performance because it is not a melting process. You can print copper in the center of a core to wick away heat and keep the outside of the mold stainless steel, for example.
You also don't have to print an entire part. Start with a large chunk of material and then only print the features that will benefit from additive—for example, printing a copper core over the top of the die face.
If you don't have to print it, don't. Use the appropriate tools in your arsenal.
Related Content
Mold Builder Uses Metal 3D Printing to Bridge Medical Product Development to Production
Westminster Tool uses metal additive manufacturing for medical device OEM, taking lessons learned from R&D in the prototype mold phase to full-scale production molding in a fraction of the time.
Read MoreMMT Chats: The Connection Between Additive Manufacturing Education and ROI
This MMT Chat continues the conversation with Action Mold and Machining, as two members of the Additive Manufacturing team dig a little deeper into AM education, AM’s return on investment and the facility and equipment requirements to implement AM properly.
Read MoreHow to Make Data Work for Mold Productivity and Performance
The use of digital workflows improves the impact of mold design libraries, conformal cooling and machine learning.
Read MoreHow to Supply Cooling to Additive Tooling
Additive tooling provides limitless options for cooling a mold’s difficult-to-cool areas.
Read MoreRead Next
Cutter Considerations for Hybrid Additive Manufacturing
Four tips for applying the right cutting tools in hybrid additive manufacturing.
Read MoreHow to Improve Mold Venting with Metal Additive Manufacturing
Patented 3D-printed mold insert design rapidly evacuates gases while preventing plastic flash-through, eliminates costly maintenance and need for press-side temperature-control units.
Read MoreHow to Design a Mold with Additive Tooling
Designing molds with additive tooling implementation in mind requires blending traditional mold standards with innovative new ideas of what is possible to push the limits of mold performance.
Read More