Access to CAD-to-CAM Workflow with Advanced Modeling Tools Accelerate Solid Model Preparation
Hexagon is helping mold and die manufacturers improve their productivity by giving every WORKNC CAM software user access to its CAD-to-CAM workflow, Designer, to ensure that components are both feasible and optimized for efficient production.
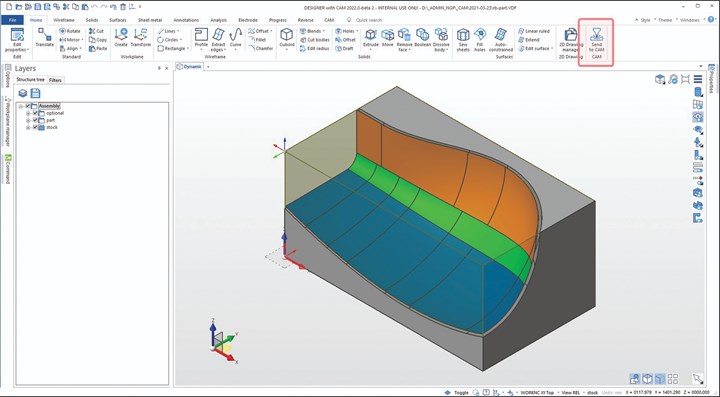
Designer sent to CAM. Photo Credit, all images: Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence
Hexagon’s Manufacturing Intelligence division reports that it is providing all mold and die shops using its WORKNC CAM software with immediate access to its model preparation software, Designer, integrating production workflows from any CAD model format to CAM so users can machine parts more efficiently and avoid costly errors.
Hexagon notes that, by providing WORKNC customers with access to its robust and fully featured CAD application, Designer companion, Hexagon has made it easier to prepare any mold or die for machining while simplifying the challenge of working with a wide range of file types from different CAD tools used in the industry. Because the software offers specialist tools for mold-and-die engineering out of the box, the resulting workflow is said to significantly simplify the preparation of models that are both feasible and optimized for efficient production.
Further, introducing universal access to CAD preparation is said to help users to accelerate the process of healing missing faces, extending surfaces and capping holes and pockets in preparation for manufacturing. Direct modeling functions are also considered to be easier, more intuitive and less limiting than traditional parametric modeling. Hexagon says users are also able to employ a hybrid design approach that combines surface and solid entities through direct-modeling techniques. Once ready, users can send solid models directly from Designer to WORKNC, and the integrated workflow will save them time by ensuring accurate models are automatically assigned as stock and part.
Once a model is prepared, new advances in WORKNC’s programming capabilities reduce the time spent calculating toolpaths and help to generate faster and more efficient code for reduced cycle times. Used with a spiral toolpath option, the software’s three-axis parallel finishing strategy supports compensation for any tool shape, including lens cutters, barrel cutters and any other circle-segment tools. On average, Z-level cutting toolpaths using this strategy can now be calculated four times faster than in previous versions of the software, according to Hexagon.
New strategies for machining with Advanced Toolform technology, which supports programming with any tool shape for greater efficiency, are central to new developments in WORKNC. New five-axis offset, parallel finishing and curve-machining strategies can be used to generate fast, reliable toolpaths with barrel cutters, lens cutters and other user-defined shapes for improved surface finish and reduced cycle times.

Further, contour re-machining with Advanced Toolform reportedly makes rest finishing parts faster and more precise by enabling any tool shape to be selected. This re-machining strategy aids users to automatically machine material remaining after an initial roughing operation using increasingly smaller cutting tools for subsequent roughing and finishing operations, for more accurate detection of remaining material even when previous processes used circle-segment tools, smoothing radius parameters or were applied from a different angle. The calculation of the toolpath is now also three times faster than in the previous version of the software when using the updated 3D stock model as a reference.
WORKNC also offers the latest in curve-profiling technology for wireframe machining by providing robust tool-radius compensation capabilities. The curve-profiling strategy enables the management of tool-radius compensation parameters that can be used to adjust for tool wear at the machine-tool control without the need to return to the CAM department for reprogramming.
For enhanced simulation and verification capability, the latest release of WORKNC also enhances workflow integration with NCSIMUL, Hexagon’s machine-simulation software. Numerical control (NC) code and links for toolpaths generated by WORKNC can be easily imported into NCSIMUL to simulate the manufacturing process on a target machine type and validate it for optimal, risk-free production.
Related Content
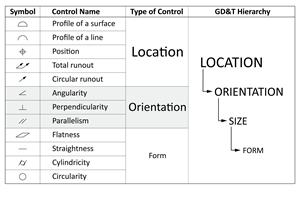
Tolerancing in Mold Design, Part 2: Using GD&T to Address Conventional Tolerancing Issues
Mold designers can achieve a single interpretation of workpiece functionality when following the American Society of Mechanical Engineers Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing standard.
Read MoreIt Starts With the Part: A Plastic Part Checklist Ensures Good Mold Design
All successful mold build projects start with examining the part to be molded to ensure it is moldable and will meet the customers' production objectives.
Read MoreFour Micro Tooling Considerations
Issues involving gating, ejection, mold splits and direction of pull are of special concern when it comes to micro tooling.
Read MoreHow a Small Programming Change Cuts Cycle Time in Half
Overriding the CAM system when milling a series of lifter pockets helps to improve metal removal rate and increase feed rates.
Read MoreRead Next
How to Use Continuing Education to Remain Competitive in Moldmaking
Continued training helps moldmakers make tooling decisions and properly use the latest cutting tool to efficiently machine high-quality molds.
Read MoreAre You a Moldmaker Considering 3D Printing? Consider the 3D Printing Workshop at NPE2024
Presentations will cover 3D printing for mold tooling, material innovation, product development, bridge production and full-scale, high-volume additive manufacturing.
Read MoreReasons to Use Fiber Lasers for Mold Cleaning
Fiber lasers offer a simplicity, speed, control and portability, minimizing mold cleaning risks.
Read More