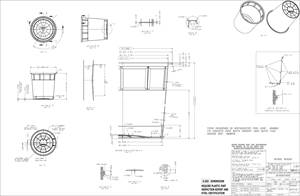
Siemens, Stratasys Partner to Incorporate Additive Manufacturing into Volume Production
The formal partnership aims to strengthen and expand the benefits of 3D printing in manufacturing value chain, with the aerospace, automotive and tooling industries expected to benefit first.
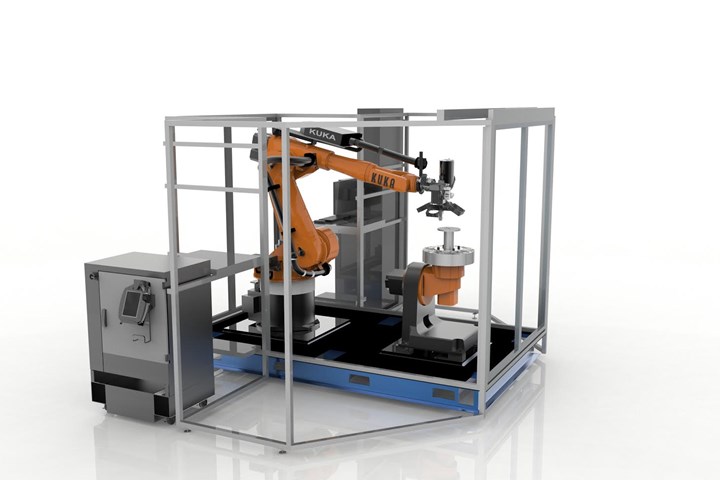

At the core of the 3D Demonstrator is said to be Stratasys’ advanced FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) Additive Manufacturing technology synchronized to complex multi-axis motion.
Stratasys Ltd. (Eden Prairie, Minnesota) and Siemens (Plano, Texas) have announced a formal partnership to integrate Siemens Digital Factory solutions with Stratasys additive manufacturing (AM) solutions. The partnership is intended to lay the foundation for the two companies to fulfill a shared vision of incorporating AM into the traditional manufacturing workflow in order to help it to become a universally-recognized production practice which can benefit multiple industries, including aerospace, automotive, transportation, energy and industrial tooling.
Both companies say there have been multiple collaborative projects including the direct link from Siemens’ NX software for CAD/CAM/CAE to Stratasys GrabCAD Print platform—enabling what is said to be a seamless design-to-3D print workflow—and the previewed Stratasys Robotic Composite 3D Demonstrator that incorporates Siemens product lifecycle management (PLM) software and its motion control and CNC automation technologies, to produce strong, lightweight performance parts.
“Siemens is enthusiastic about this partnership with Stratasys and the opportunity to help our customers adopt a new manufacturing mindset that we believe will result in better products produced more economically and delivered more efficiently,” says Zvi Feuer, SVP Manufacturing Engineering Software, Siemens PLM Software. “We are committed to the industrialization of AM with all of its unique advantages, including complex part geometries, on-demand production and mass customization. This relationship helps set the course for continued innovation and leadership through the tight integration of our product lines and through collaboration on comprehensive AM solutions.”
“We believe that the impact on production practices will begin sooner rather than later with the aerospace, automotive and factory tooling industries expected to benefit first.”
“Siemens’ capability and commitment to the digital enterprise vision, along with its close collaboration with Stratasys, can help many industries realize shorter time-to-market, achieve flexibility in operations and improve efficiency in workflows through horizontal (machine-to-machine) and vertical (plant and top-floor to factory floor) integration,” adds Arun Jain, VP of Motion Control, Siemens Digital Factory U.S.
While AM technology has made great strides over the past years, additional criteria are required for it to take its place in volume production environments and become as commonplace as CNC. Ideally, says Siemens, AM solutions should deliver robust, repeatable and reliable operational performance with predictable properties across a broad portfolio of materials that are certifiable for specific applications and that are driven by a seamless, digital integration from design to production. Together, Stratasys and Siemens plan to address these challenges.
“With our complete 3D printing ecosystem of customer applications, hardware and software platforms, advanced material offerings and consulting services, Stratasys is uniquely positioned to help manufacturers leverage 3D printing to transform their business models,” says Dan Yalon, executive VP, Products, Stratasys. “Stratasys is excited to formalize our partnership with Siemens, and views it as a catalyst for the industrialization of AM. We believe that the impact on production practices will begin sooner rather than later with the aerospace, automotive and factory tooling industries expected to benefit first.”
At the core of the 3D Demonstrator is said to be Stratasys’ advanced FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) Additive Manufacturing technology synchronized to complex multi-axis motion. It features Stratasys extensible and scalable multi-operation architecture that provides the flexibility to integrate subtractive manufacturing, inline inspection and verification, and product finishing. According to Stratasys, its engineered materials are employed to produce structures that are optimized for weight and performance. The result is a new hybrid manufacturing approach that is reportedly unconstrained by the traditional limitations of composite layup and the layer-by-layer limitations and support material requirements of traditional 3D printing.
The new workflow for the Stratasys Robotic Composite 3D Demonstrator begins with Siemens NX software. NX enables designers to create parts to be produced on the system, simulate and evaluate the design for manufacturability and generate and send all the manufacturing instructions for part production. Throughout the manufacturing process, performance is controlled and communicated directly to the manufacturing operations management systems. The result is said to be a seamless CAD-to-product workflow that streamlines production and ensures end-to-end traceability and part quality.
The motion control for the Stratasys Robotic Composite 3D Demonstrator is also driven by the Siemens Sinumerik 840D sl CNC. The open architecture of Sinumerik control combines the strengths of Siemens NC with flexible robot kinematics. The integration with Stratasys extrusion control technologies to execute manufacturing instructions from NX CAM, results in a high degree of freedom for robotic FDM extrusion.
Related Content
Machine Hammer Peening Automates Mold Polishing
A polishing automation solution eliminates hand work, accelerates milling operations and controls surface geometries.
Read MoreIt Starts With the Part: A Plastic Part Checklist Ensures Good Mold Design
All successful mold build projects start with examining the part to be molded to ensure it is moldable and will meet the customers' production objectives.
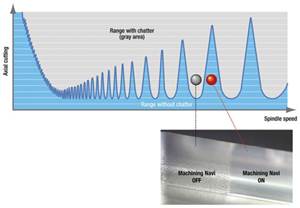
Read MoreHow to Eliminate Chatter
Here are techniques commonly used to combat chatter and guidelines to establish a foundation for optimizing the moldmaking process.
Read MoreMoldmakers Deserve a Total Production Solution
Stability, spindle speed and software are essential consideration for your moldmaking machine tool.
Read MoreRead Next
Markforged Report Suggests 3D Printing Enabled Manufacturers to Persevere Through COVID-19
Data shows that manufacturers using 3D printing were able to continue normal operations and innovate, while saving time and money.
Read MoreReasons to Use Fiber Lasers for Mold Cleaning
Fiber lasers offer a simplicity, speed, control and portability, minimizing mold cleaning risks.
Read MoreHow to Use Continuing Education to Remain Competitive in Moldmaking
Continued training helps moldmakers make tooling decisions and properly use the latest cutting tool to efficiently machine high-quality molds.
Read More