Run Silent, Run Aggressive
Reap the benefits of using vibration dampening tools in your roughing operations.
Vibration dampening tools—or silent tools as they are sometimes referred to—have been around for quite a while. Mold and die shops incorporate such tools to eliminate vibration issues associated with the long slender tools needed to machine the deep and narrow cavities of molds and dies.
Most shops apply silent tools to finish cut operations for generating smooth mold and die surfaces that require little, if any, secondary benchworking. But what these shops may not realize is that they can gain significant benefits by also using silent tools for roughing operations.
Silent tools, in particular dampened adapters, allow mold and die shops to run rough machining operations at faster cutter speeds and feeds, and take depths-of-cut that are frequently three times deeper than those possible with a comparable solid steel extended tooling assembly.
Additionally, today’s dampened adapters can work at much longer tool lengths and apply to wider ranges of materials—including stainless steels and titanium—compared to standard extended tooling assemblies.
When tools vibrate, they make noise, which is where the term silent tools originated. Dampened adapters counteract tool vibrations with passive internal systems that vibrate at different amplitudes than those being generated at the cutting edge of the tool.
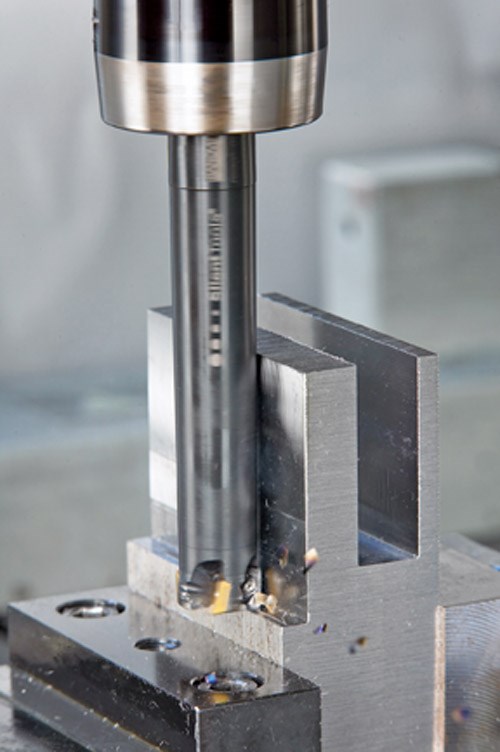
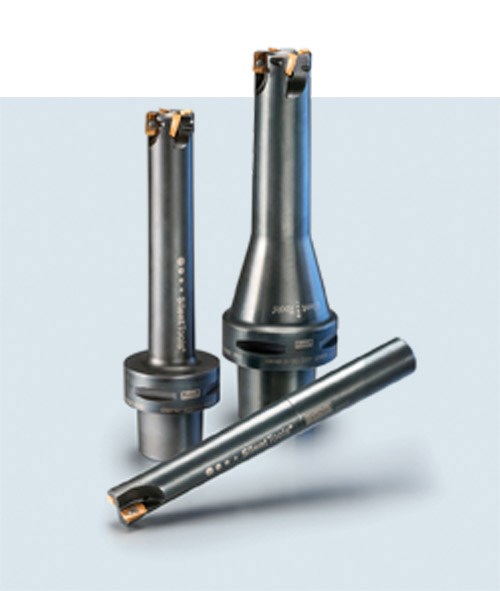
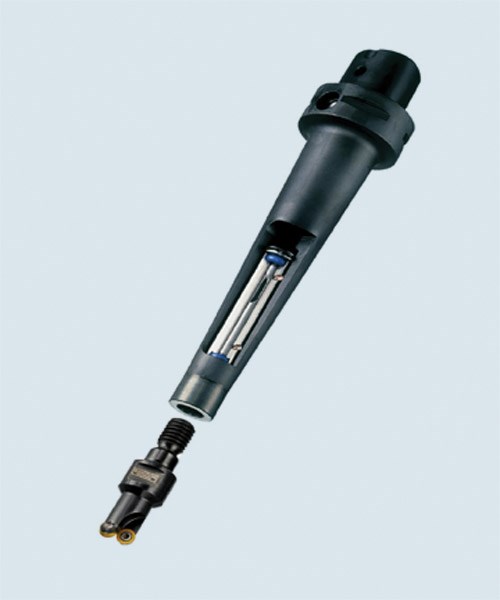
Dampened adapters are an interface between machine tool spindles and cutting tool tips. The dampened adapter and cutting tool could be a one-piece design with the cutting tool integrated into the adapter, or it could be a system where cutting tools mount to the end of the adapter and are interchangeable.
Hollowed out chambers at the front of dampened adapters house what is known as the damper. Dampers are cylindrical-shaped heavy metal slugs surrounded by and floating in oil within the chamber. They have rubber grommets attached at each end, which in turn, are attached to springs attached to the edges of the chamber.
As standard tools start to cut, they begin to vibrate at particular amplitudes, and shops basically deal with them by reducing speeds and feeds. On the other hand, when these vibrations reach the dampening mechanism of a dampened adapter, the damper begins to move up and down vibrating at an opposite amplitude. This motion occurs in milliseconds and counteracts the vibration amplitude to completely eliminate any negative affects on workpiece surfaces.
Dampening mechanisms in silent tooling are passive systems that react to vibrations to control them. This is unlike active systems that involve the introduction of external mechanical or electrical forces/vibrations that help cancel out those generated by a cutting tool. Active systems are not internal and would involve some type of outside device.
Mold and die shops not using dampened adapters must build tools out to needed lengths. But to achieve fine surface finishes, these tools have to run at incredibly light cutting data, dramatically prolonging finishing operations and overall part cycle times.
It is recommended that shops already using or considering dampened adapters should match adapter to cutting tool. Specific tooling manufacturers design their adapters to run with their cutting tools. And while some shops will mix and match, the best possible cutting performance results from pairing adapter and tools from the same manufacturer.
In addition to mold and die milling applications, dampened adapters can be used for internal turning, boring and drilling. As with milling, these products work on overhangs beyond the limitation of solid steel and solid carbide shanks. They are easy to operate and are very flexible due to the wide variety of back-end and front-end couplings available.
Related Content
Maintaining a Wire EDM Machine
To achieve the ultimate capability and level of productivity from your wire EDM on a consistent, repeatable and reliable basis, regular maintenance is a required task.
Read MoreSolving Mold Alignment Problems with the Right Alignment Lock
Correct alignment lock selection can reduce maintenance costs and molding downtime, as well as increase part quality over the mold’s entire life.
Read MoreThe Ins and Outs of Hot Runner Temperature Control
A training checklist that explains the why and how of proper hot runner temperature control and system management.
Read MoreTreatment and Disposal of Used Metalworking Fluids
With greater emphasis on fluid longevity and fluid recycling, it is important to remember that water-based metalworking fluids are “consumable” and have a finite life.
Read MoreRead Next
Cut the Chatter - Tooling Tips to Eliminate Vibration in Cavity Milling
By learning how to eliminate vibration in cavity milling operations, a typical moldmaking shop can decrease the wear and tear on its tools, as well as boost its level of productivity.
Read MoreHow to Use Strategic Planning Tools, Data to Manage the Human Side of Business
Q&A with Marion Wells, MMT EAB member and founder of Human Asset Management.
Read MoreHow to Use Continuing Education to Remain Competitive in Moldmaking
Continued training helps moldmakers make tooling decisions and properly use the latest cutting tool to efficiently machine high-quality molds.
Read More.png;maxWidth=970;quality=90)











.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)