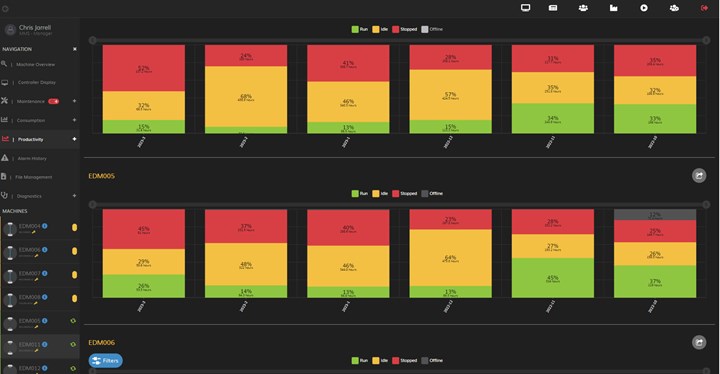
Remote monitoring systems provide accurate and up-to-date data on machine utilization and production rates. Photos Credit, all images: MC Machinery Systems
Manufacturing is more data-driven than many realize. The only reliable way to identify performance-impacting problems is through data analytics, which can reveal ways to maximize capacity and uptime, prioritize opportunities, test assumptions, find waste and guide continuous improvement processes.
Remote machine monitoring is collecting and analyzing data from machines in real time without human intervention. When considering what remote monitoring system is right for their business, moldmakers should evaluate their specific needs, including the desired level of data collection, whether that data is provided in real time, user-friendliness, scalability and customer support.
For moldmakers, remote machine monitoring can provide several benefits, including improved efficiency, productivity and quality, reduced costs and increased safety.
Capturing Data
Mold builders can gain insight into six key areas with remote machine monitoring:
- Real-time performance monitoring. Remote monitoring systems enable mold builders to track the performance of their machines in real time. They can gather data on parameters, including machine status and production rates. This information provides valuable insight into machine efficiency, productivity and potential production issues. For example, users can receive an alert so they can react immediately if the machines run unattended and an alarm occurs. This prevents lost production time due to interrupted jobs not being addressed until someone on-site notices the stopped machine.
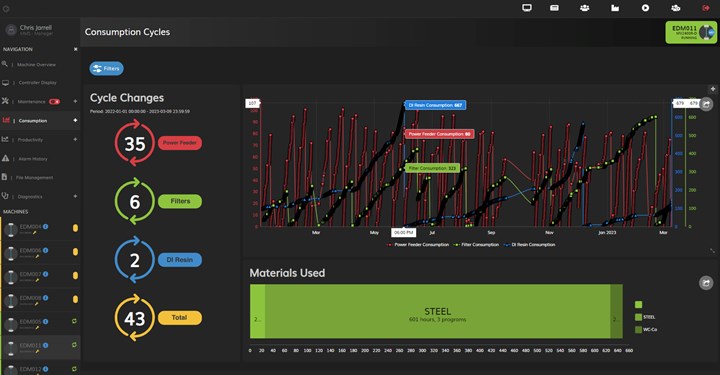
- Predictive and preventive maintenance. Mold builders can detect abnormalities or deviations from normal operating conditions by continuously monitoring machine data remotely. This enables early detection of potential issues such as equipment malfunctions or process inefficiencies. Identifying these problems early and scheduling preventive maintenance activities reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns and downtime. Analytics from the hardware maintenance timers, machine data and alarm history can help predict any potential problems.
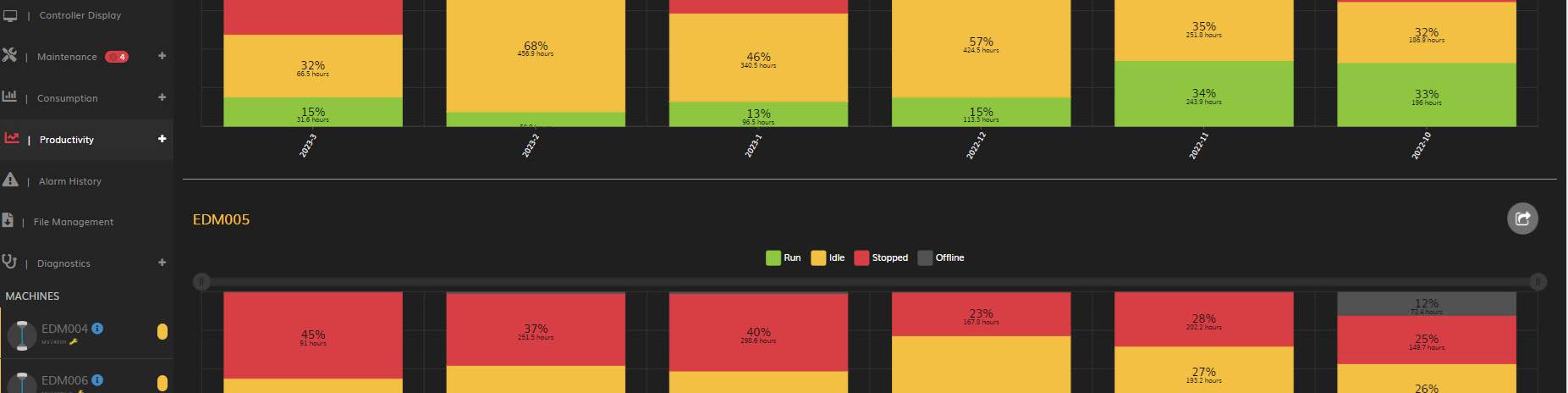
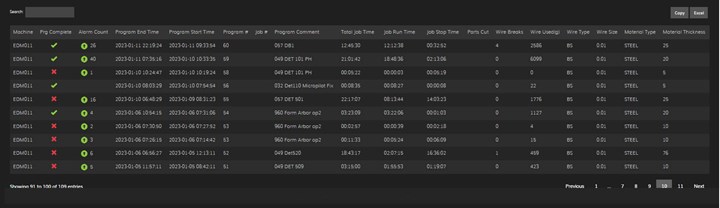
- Optimized production planning. Remote monitoring provides accurate and up-to-date data on machine utilization and production rates. This information allows for better production planning and scheduling, including identifying bottlenecks, optimizing machine allocation and making informed decisions to maximize productivity and meet delivery deadlines. For example, by viewing the program history to see when jobs were run and how long they took to complete, operators can better schedule which jobs are run in the machine during manned versus unmanned shifts.
To make informed decisions, moldmakers must effectively capture, harness and secure data.
- Improved efficiency and productivity. Remote monitoring systems provide valuable data on machine utilization, downtime and performance metrics. This data can identify opportunities to optimize the process, reduce idle time and improve overall machine efficiency. Operators can track key performance indicators and implement measures to increase productivity, such as reducing setup times or improving tool changeover processes. For example, by viewing when a block of heavy stopped time was reported, users can filter the program and alarm history to see which programs generated the most stopped time. This can help operators determine if corrective action may prevent the same occurrence from happening again.
- Remote troubleshooting and support. Mold builders can access machine controls and diagnostics remotely. This capability allows for remote troubleshooting, reducing the need for on-site visits and minimizing downtime associated with equipment issues. For example, if the user has a problem with a program, he or she would typically have to email the program file to the support team and wait for them to review, edit and return it — taking hours for a resolution that the remote support team could handle in just a few minutes.
- Enhanced quality control. These systems can capture and analyze data related to process parameters, burn/cut conditions, operation stability and alarms. Monitoring these variables ensures that the production process remains within nominal operating conditions. Any deviations can be detected and corrected promptly, improving product quality and reducing scrap or rework. One example is monitoring the burn/cut condition remotely. If a user notices that it is unstable or having problems, they are able to remotely connect to their machine controller and make adjustments as if they were in front of the machine.
Saving Costs
Remote monitoring systems help mold builders optimize machine utilization, reduce unplanned downtime and improve overall efficiency. Shops can also save costs by minimizing production disruptions, optimizing maintenance schedules and preventing costly breakdowns.
Additionally, remotely monitoring machines reduces the need for a physical presence on the shop floor, potentially saving travel costs and enabling centralized monitoring of multiple machines or production facilities.
Mold builders can track machine performance in real time. They can gather data on parameters such as machine status and production rates.
Securing Data
Now that you have all of this data from a cloud-based remote machine monitoring system, you must secure it. Consider the following measures to ensure data security:
- Data encryption. Employ robust encryption techniques to protect data transmitted between machines and the cloud platform. Encryption ensures that the data remains unreadable to unauthorized individuals even if intercepted.
- Secure authentication. Implement strong authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. This can include multifactor authentication, strong passwords and secure, token-based access.
- Role-based access control. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to grant specific permissions and restrict access based on user roles and responsibilities. Only authorized individuals can access and interact with the monitoring system.
- Secure communication. Use secure communication protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Shell (SSH), for data transmission between machines and the cloud platform. These protocols establish secure channels and protect against eavesdropping or tampering.
- Intrusion detection and prevention. Employ intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) to monitor network traffic, detect potential threats or attacks and take appropriate action to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Regular updates and patch management. Keep all software components, including the monitoring system and associated software, up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Regularly applying patches helps address known vulnerabilities and strengthens the overall security posture.
- Security monitoring and auditing. Implement robust security monitoring and auditing mechanisms to track system activities, detect anomalies and identify potential security incidents. This can involve monitoring log files, analyzing system behavior, and employing security information and event management (SIEM) tools.
- Data privacy and compliance. Ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or industry-specific standards. Implement appropriate data anonymization or pseudonymization techniques when necessary.
- Vendor security evaluation. If using a third-party cloud platform or monitoring solution, thoroughly evaluate the vendor's security practices and certifications. Verify that they have appropriate security measures and adhere to industry best practices.
- Employee awareness and training. Educate employees about security best practices, such as strong password management, phishing awareness and data handling protocols. Promote a security-conscious culture within the organization to minimize the risk of human error or insider threats.
To make informed decisions, moldmakers must effectively capture, harness and secure data. No matter the size of the manufacturing operation, data is critical to efficiency and growth. Remote machine monitoring can help.
Related Content
Precision Meets Innovation at IMTS 2024
After attending IMTS, it's clear that the integration of advanced technologies is ready to enhance precision, efficiency and automation in mold manufacturing processes. It’s a massive event, so here’s a glimpse of what the MMT team experienced firsthand.
Read MoreHow to Produce More Accurate Molds and Reduce Rework
Patented micro-milling process for manufacturing steel plate flat and parallel helps mold builders shorten mold build times and increase accuracy.
Read MoreSolving Mold Alignment Problems with the Right Alignment Lock
Correct alignment lock selection can reduce maintenance costs and molding downtime, as well as increase part quality over the mold’s entire life.
Read MoreRead Next
Single-Brand EDM Arsenal Helps Moldmaker Speed Services for Diverse Clientele
Microtech Precision sticks with Mitsubishi EDM (and milling) technology to optimize machining capabilities for molds, dies and more.
Read MoreUsing Real-Time Production Data
One approach to smart manufacturing is using a single, cloud-based tool for production scheduling, job tracking and CNC machine monitoring.
Read More5 Sinker EDM Advancements
Speed, machine design, software, artificial intelligence and automation help maximize sinker EDM productivity.
Read More