Material used for mold bases is pretty straight forward. The materials are common and have been around for a long time; however, choosing the right material will help save time and money. Generally, mold base material can be broken down into three categories: hot rolled steel, chrome-moly materials and stainless steel.
Hot rolled steel materials vary from low carbon steel (A-36 or 1020) up to medium carbon steel (1045 or 1050). These steels are easy to machine and have reasonable tensile strength. They are easy to find and are very cost-friendly. They are usually chosen when the customer has very low production runs associated with the project.
Chrome-moly materials range (from 4130, P20, 4140 and etc.) have a hardness range from 28-34 HRC and have good mechanical properties. They are ideal for cavity and core plates as well as other plates required in the mold base. They can be machined fairly well; however, in some cases with heavy machining or grinding, a need to stress relieve the material may be required.
Stainless steel (a modified 420 F material that is used for holder block applications) is pre-hardened to 30-35 HRC. It offers good corrosion resistance and has very good machinability. The material is very stable and does not require stress relieving. In applications where humidity is a problem or corrosive material is being used, this material works well.
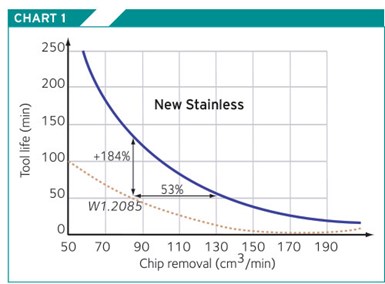
Chart 1.
Photo Credit, all photos: International Mold Steel Inc.
There are two additional mold base materials to consider. The first material falls in the stainless steel category (see Chart 1). It is an improved 420 F material currently competing with 1.2085 in Europe. It has excellent machining qualities and does not need to be stress relieved. By lowering the carbon and chrome content, this material has improved machinability, and has 10 to 15% better thermal conductivity than the 420 F material currently being used (see Charts 2, 3).
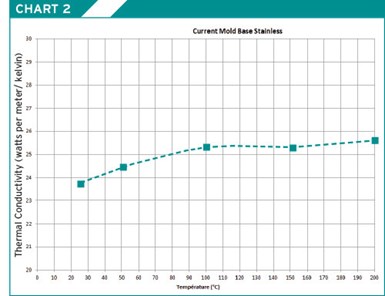
Chart 2.
Keep in mind that having an advantage with regards to thermal conductivity depends on how large the part is, as well as the number of cavities involved. Customers are always trying to find ways to lower cycle time, and this is one way to help lower that value.
This material also benefits from tightened rolling tolerances, which means a mill can deliver higher dimensional quality steel to the end user, saving them time and money. For example,a popular stainless material requires around 6mm oversize to finish to the desired dimension. The improved rolling capabilities can reduce the amount of oversize needed by about 20 to 33%, lowering costs for customers. The mill can roll material up to 5.5 inches thick and up to 96 inches wide.
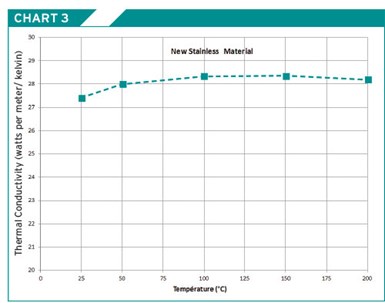
Chart 3.
The second material is a P20-type material that has replaced 4140 and P20 by two large mold base manufacturers in Europe. The reason for the switch was better machinability, and because this material is very stable—even during heavy machining and grinding—there is no need for stress relieving. Gun drilling is also much easier because the material does not have hard spots. This material is supplied 30-35 HRC and possesses a unique chemistry. It also is heat treated differently than other types of quench and tempered steels.
A fast quench method of heat treatment is applied. The material comes off the rolling mill and immediately receives the fastest quench possible. There is no tempering process with this material. This process gives this material its unique properties. Chart 4 shows the comparison to 4140 HT mold quality material.
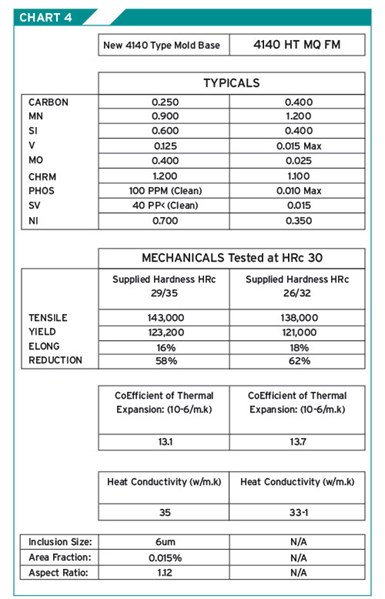
Chart 4.
So, when looking to decrease the costs and improve the profitability of your next job, don’t forget to consider the impact of your mold base material selection. Hopefully considering these aforementioned factors and new developments in mold base materials will help with your decision-making process.
Related Content
How to Determine the Proper Vent Depth
Vent depth is critical to optimizing mold performance, so here is one approach to finding that elusive right number.
Read MoreMaking Quick and Easy Kaizen Work for Your Shop
Within each person is unlimited creative potential to improve shop operations.
Read MoreMold Design Review: The Complete Checklist
Gerardo (Jerry) Miranda III, former global tooling manager for Oakley sunglasses, reshares his complete mold design checklist, an essential part of the product time and cost-to-market process.
Read MoreMachining Center Spindles: What You Need to Know
Why and how to research spindle technology before purchasing a machining center.
Read MoreRead Next
Three Considerations for Mold Steel Selection
Although a big challenge is selecting the right steel for the right job, steel selection has never been better in regards to quality, price and delivery speed. Here is a simple checklist when selecting your next mold steel.
Read MoreHow to Use Continuing Education to Remain Competitive in Moldmaking
Continued training helps moldmakers make tooling decisions and properly use the latest cutting tool to efficiently machine high-quality molds.
Read MoreAre You a Moldmaker Considering 3D Printing? Consider the 3D Printing Workshop at NPE2024
Presentations will cover 3D printing for mold tooling, material innovation, product development, bridge production and full-scale, high-volume additive manufacturing.
Read More