Electrical Discharge Machining
Moldmakers rely on electrical discharge machining (EDM) routinely. EDM refers to wire, sinker and small-hole EDM. Sinker includes an electrode and a workpiece both submerged in dielectric fluid; wire uses a thin wire to cut with electricity; and, with small hole an electrode is a cylinder used to machine a hole. Considerations for EDM efficiency include depth, accuracy and finish, and components to consider include drives, generator, programming system and flushing. Other facets include wires, electrodes, graphite, filters and fluids.

ESSENTIAL READING
VIEW ALLHow to Improve Your Current Efficiency Rate
An alternative approach to taking on more EDM-intensive work when technology and personnel investment is not an option.
Read MoreMaintaining a Wire EDM Machine
To achieve the ultimate capability and level of productivity from your wire EDM on a consistent, repeatable and reliable basis, regular maintenance is a required task.
Read MoreSoft Wired: Cutting High Taper Angles with Wire EDM
Examine the wire’s properties to determine the right one for achieving the best cut.
Read MoreThe Lean Dream Team: How to Achieve High-Cavitation, Critical Dimension Molds
Incorporating multiple automation technologies enables Industrial Molds to produce and repair highly complex, precision molds with a very lean team.
Read MoreCombining Customized Software with CMM Reduces Production Bottleneck
In order to reduce downtime on its EDM and CNC machines when setting up new jobs, moldmaker Kavia Tooling turned to a coordinate measuring machine from Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence to create an offline zero transfer system ahead of the manufacturing process for parts and electrodes.
Read MoreHow to EDM Steel and Copper Alloy Simultaneously
A strategy for machining details when the part geometry falls across multiple workpiece materials.
Read MoreLatest EDM News And Updates
Integrated CAD/CAM Streamlines Electrode Manufacture, Improves Quality
A focus on electrode design and automation helps toolroom improve efficiency, reduce tooling costs and deliver higher quality products.
Read MoreSmall-Hole EDM With Automation for Moldmakers
IMTS2024: Belmont Equipment & Technologies offers its SY series high-speed CNC EDM drills for customizable, small-hole drills. These are useful in moldmaking for vent holes and ejector pin hole applications.
Read MoreEDM, Precision Milling, 3D Printing Improves Accuracy, Reduces Machining Time
IMTS 2024: MC Machinery Systems showcases an array of EDM and precision milling tools, as well as a wire laser metal 3D printer, all of which have the capacity to meet moldmaking needs.
Read MoreTechnology Review and Sourcing Guide 2024: EDM
Moldmakers rely on electrical discharge machining (EDM) routinely. EDM refers to wire, sinker and small-hole EDM. Access this exclusive, online-only content, including a suppliers list, EDM products, services and more.
Read MoreEDM Graphite Line for High-End EDM Machining
IMTS 2024: Mersen offers its complete family of EDM graphite, including its ultra-fine DS4 graphite. The graphite is used as the electrode which acts as a “cutting tool” in the sinker EDM, a machining process often used by moldmakers.
Read MoreQuality Tool & Die Enhances Performance With Advanced EDM and Milling Technologies
The adoption of Mitsubishi wire and sinker EDMs, along with the OPS Ingersoll five-axis milling machine with automated cells, has enabled unmanned operations and improved precision. As a result, QTD has expanded its facility, grown its workforce and increased its business by 10-15% annually.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
How to Improve Your Current Efficiency Rate
An alternative approach to taking on more EDM-intensive work when technology and personnel investment is not an option.
Read MoreExtensive Evaluations Build The Plastek Group’s EDM Arsenal
Sinker and wire EDMs selected for speed, volumetric accuracy, surface finish, reliability, cost of ownership and extensive warranty.
Read MoreMachine Monitoring Platform Improves Machine Utilization, On-Time Delivery
Using data from a machine monitoring platform, Westminster Tool added almost 75 hours of capacity per week by shortening warmups and starting CNC and EDM machines sooner.
Read MoreDiscover Metalworking Technologies Targeted to Mold Shops
What EDM, automation and machining technologies are currently available to the mold manufacturing industry? MMT has compiled a list of some of the latest.
Read MoreMMT Chats: 4 Keys to a Successful Mold-Building Operation: Innovation, Transparency, Accessibility and Relationship
MoldMaking Technology Editorial Director Christina Fuges chats with Steve Michon, co-owner of Zero Tolerance in Clinton Township, Michigan, about the excitement of solving problems, the benefits of showing gratitude, the real struggle with delegation and the importance of staying on top of technology. This episode is brought to you by ISCAR with New Ideas for Machining Intelligently.
WatchTechnology and Sourcing Guide 2023: EDM
EDM refers to wire, sinker and small-hole electrical discharge machining. Components include drives, generators, programming, flushing, wires, electrodes, graphite, filters and fluids.
Read MoreFAQ: EDM
What is EDM?
EDM stands for Electrical Discharge Machining. A good way to describe the material erosion process of an electrical discharge machine is to think of the EDM spark as a shovel. Whether you are digging a hole or electrically removing material to form a cavity with an EDM, you remove material one shovel, or one spark, at a time. To dig a hole/cavity faster, you can use a bigger shovel (more power) or shovel faster (shorter pauses between sparks) or use a different-shaped shovel (electrical waveform).
When you consider that the speed of the EDM process may vary from 1,000 to 150,000 sparks per second, a machine that helps you choose the correct waveform, select the maximum power allowable by geometry, and automatically adjust the flush and cooling time between sparks is a pretty difficult machine to beat.
The EDM process, much like other metal-removal processes, presents two main difficulties that must be overcome: heat and contamination. Each tiny spark creates heat, and the more power and the higher the frequency of the spark, the more heat is created. A good spark should take a large shovel out of the workpiece and a very small piece of the electrode.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
Why use EDM?
The need for accuracy, finishes and repeatability are the biggest challenges moldmakers deal with. Electrode accuracy is incredibly important for high productivity and good product finishes. If an electrode is off by only 0.2", it will cause metal removal on one side of the cavity to work harder, leading to excessive burn time on the other side. Therefore, electrode manufacturing with better accuracy will help increase productivity and decrease burn times.
Taking advantage of the latest EDM technology will allow you to remain competitive while improving surface finishes and accuracy—in addition to reducing cycle times in your shop.
Source: Burning Bright
How do you maintain a wire EDM machine?
Due to the electro-mechanical nature of wire EDM machines, there are several items in normal operation that routinely wear and require cleaning and/or replacement. If certain machine components are not properly cared for, machining speeds and accuracies will rapidly decay.
The most important reason to properly schedule and perform this routine wire EDM maintenance is to ensure consistent and repeatable machining results for the aforementioned machine traits of speed, accuracy and surface finish. This level of maintenance also prevents machine failure and unexpected machine downtime.
There are several wire EDM machine tool manufacturers, and there are some significant differences in the machine design of each. But the importance and type of basic items that need to be maintained on all wire EDMs are very similar. When planning and scheduling wire EDM machine maintenance, required actions can be grouped into short interval and long interval items.
Short interval items vary in occurrence from weekly to monthly.
- Automatic Wire Threading System
- Power Contacts
- Belts and Rollers
- Brake/Clutch Roller
- Wire Guides
- Wire Alignment
- Wire Collection Box
- Machine Seals
- General Cleaning
Long interval items vary from bi-monthly to yearly.
- Machine Filters
- De-ionization Resin
- Water Level
- Belts, Rollers and Pulleys
- Wire Choppers
- Cabinet Filters
- Machine Seals
- Machine Floats
- Water Reservoir
- Machine Lubrication
Good cleaning habits and care of a wire EDM machine is highly recommended. Regular and systematic cleaning of the machine also can extend the life of some consumable items.
Source: Maintaining a Wire EDM Machine.
What is EDM process priority?
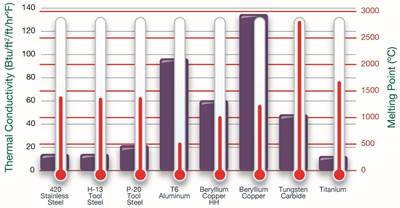
Since EDM is a thermal process, the melting point/temperature and thermal conductivity of the work metal can create difficulties for the EDM operator. Knowing the elements that make up the material will help determine the optimum melting point/temperature and thermal conductivity.
The work metal’s melting temperature and thermal conductivity require the EDM operator to adjust on-time, amperage, polarity, voltage and off-time parameters, which differ from one work metal to another. If the same EDM approach is used regardless of work metal, the end results could be vastly different.
The EDM process priority refers to the desired metal removal rate, electrode wear and surface finish. This information helps the operator determine the best approach to the job. However, regardless of what is identified as the main priority, electrode size, detail and shape must be known in order to determine the appropriate machine parameters, including amperage, on time, off time, voltage and polarity.
Sources: