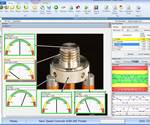
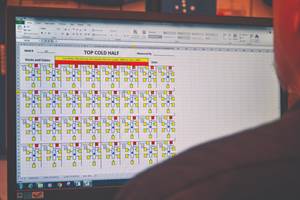
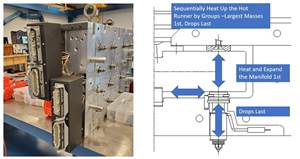
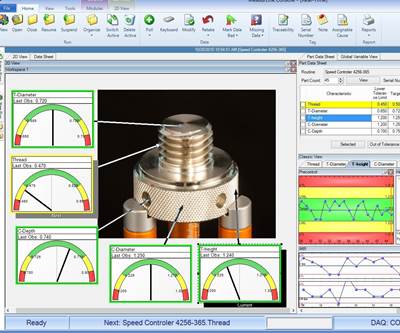
New sensor technology is changing the way many different types of measurements are acquired. These innovative sensors are robust enough to be used on the shop floor and integrated into larger measurement equipment, such as CMMs, vision systems and form units. Source (All Images) | Mitutoyo America Corp.
Intelligent moldmaking has advanced significantly due to the increased adoption of intelligent manufacturing practices driven by the challenges posed during the pandemic, including the loss of skilled labor and the need for rapid adaptation to new working conditions. However, it has also presented opportunities for companies to onboard talent remotely and leverage diverse experiences to drive innovation. While moldmakers lost skilled labor to early retirements during the pandemic, they also gained the ability to onboard engineers remotely. This flexibility has brought fresh perspectives and accelerated the adoption of intelligent manufacturing practices.
The integration of process and measurement data, along with advanced measurement sensors, has improved mold component compliance with customer requirements, reduced waste and rework and increased overall efficiency.
Here, we’ll highlight the impact of seven measurement innovation areas for the moldmaking process.
1. Cloud-Based Solutions
One of the most significant changes over the past five years has been the accelerated adoption of cloud-based technologies. The pandemic forced many once-resistant companies to transition to remote working environments and cloud-based data storage.
This shift has enabled moldmakers to implement sophisticated data collection and management systems more rapidly than anticipated. The transition not only facilitated real-time data sharing and collaboration but also paved the way for integrating advanced modules into existing ERP systems.
2. SPC Software
Statistical Process Control (SPC) software has also seen substantial improvements, driven by the high demand for more integrated and comprehensive data management solutions. Modern ERP systems now incorporate SPC modules that were once handled by separate pieces of software, streamlining operations and reducing the need for complex IT integrations.
Previously, SPC analysis was a siloed function requiring IT bridges. Now, companies expect and demand SPC capabilities within their ERP systems, promoting seamless data flow and real-time process control.

New SPC and data management software provides a comprehensive solution for critical measurement data and information in real-time. This type of software integrates SPC into the measuring process itself, making data management from all different types of instruments much faster and more efficient.
3. AI and Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, including moldmaking. AI-powered predictive analytics have enhanced manufacturers’ ability to foresee defects and optimize processes. While machine learning insights were long a part of SPC, the broader acceptance of and trust in AI technologies has accelerated its adoption.
Moldmakers have been using predictive algorithms for years, but the acceptance of AI has made it easier to implement and trust these systems. This shift has enabled manufacturers to make significant improvements in process accuracy and efficiency.
The integration of process and measurement data, along with advanced measurement sensors, has improved mold component compliance with customer requirements, reduced waste and rework and increased overall efficiency.
4. Sensors
Sensor technology has advanced dramatically over the past five years, particularly in the realm of measurement accuracy and integration. Line scanners, once confined to QC labs, are now adaptable and robust enough to be used directly on the shop floor and even integrated into machine tools. This development has eliminated the need for time-consuming part transfers to QC labs, enabling real-time, in-line measurements.
Line scanners and other sensors have become more accurate and resilient, allowing them to be used in the production environment. This integration has significantly reduced downtime and improved measurement accuracy.
5. Training
As the moldmaking industry adopts more sophisticated technologies, the need for skilled personnel who can operate and manage these systems has grown. Training programs now emphasize proficiency in various CAD/CAM software and the ability to adapt to different platforms.
Modern moldmakers must work with multiple CAD/CAM systems and possess a flexible mindset to adapt to new tools and technologies. This versatility is essential for maximizing the benefits of intelligent manufacturing.
6. Polishing and Surface Treatment

The latest models of measurement instruments, such as indicators, micrometers, calipers and linear height gages, now come equipped with different types of data output to make acquiring measurement data even faster and more reliable.
Polishing remains a critical step in moldmaking, requiring precise measurements to ensure consistency and quality. Advances in sensor accuracy have improved the ability to measure and control material removal during polishing, leading to more consistent results and reduced rework.
State-of-the-art line scanners and other sensors enable moldmakers to measure parts before and after polishing with greater precision. This capability ensures that the right amount of material remains for surface treatments, minimizing the need for rework and reducing scrap rates.
7. CAD/CAM
AI has also revolutionized CAD/CAM software by optimizing tool paths and machining strategies. This technology leverages community-based learning and vast data sets to generate more efficient machining processes, particularly for complex, non-prismatic shapes common in moldmaking.
With an AI boost, the latest CAD/CAM programs determine the best tool paths by analyzing thousands of similar operations, improving efficiency and accuracy. This capability is particularly valuable for the intricate geometries involved in moldmaking.
Further Intelligence Integration
The journey towards fully implementing intelligent manufacturing in moldmaking is ongoing. The next frontier involves further integrating AI, continuing to enhance sensor capabilities, and additional streamlining of data management processes. Moldmakers increasingly realize they must remain agile and open to adopting these new technologies to stay competitive.
The mindset toward intelligent manufacturing has shifted from a long-term goal to an immediate necessity. Companies that embrace this change will lead the way in creating future moldmaking process and measurement advances.
Related Content
What You Need to Know About Hot Runner Systems and How to Optimize Their Performance
How to make the most out of the hot runner design, function and performance.
Read MoreWhat is Scientific Maintenance? Part 2
Part two of this three-part series explains specific data that toolrooms must collect, analyze and use to truly advance to a scientific maintenance culture where you can measure real data and drive decisions.
Read MoreThe Ins and Outs of Hot Runner Temperature Control
A training checklist that explains the why and how of proper hot runner temperature control and system management.
Read MoreMachine Hammer Peening Automates Mold Polishing
A polishing automation solution eliminates hand work, accelerates milling operations and controls surface geometries.
Read MoreRead Next
Dynamic Tool Corporation – Creating the Team to Move Moldmaking Into the Future
For 40+ years, Dynamic Tool Corp. has offered precision tooling, emphasizing education, mentoring and innovation. The company is committed to excellence, integrity, safety and customer service, as well as inspiring growth and quality in manufacturing.
Read MoreProcess and Measurement Data Aid Intelligent Moldmaking
Collecting and using measurement data ensures that mold components can meet customer specifications and reduces scrap and rework.
Read MoreCombining Innovation and Artistry to Build Complex, Precision, Multi-Cavity Molds
This Florida mold builder is about high-performance, high-precision moldmaking by blending craftsmanship with technology.
Read More